
[ad_1]
A research printed within the journal PLOS Pathogens finds that agricultural land use and fowl actions are the main elements accountable for outbreaks of West Nile virus in Europe.
 Examine: West Nile virus unfold in Europe: Phylogeographic sample evaluation and key drivers. Picture Credit score: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
Examine: West Nile virus unfold in Europe: Phylogeographic sample evaluation and key drivers. Picture Credit score: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
Background
Human and animal infections by mosquito-borne viruses have change into a significant public well being concern worldwide. In Europe, the unfold of the West Nile virus (WNV) has been progressively growing in lots of geographical areas over the previous many years. This virus could cause extreme an infection in people.
WNV is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus transmitted to people and animals by way of mosquitoes as vectors and birds as amplifying reservoir hosts. 9 distinct lineages of WNV have been recognized worldwide, with WNV-1 and WNV-2 being probably the most predominantly recognized strains in people and animals. To date, strains WNV-3 to WNV-9 have been detected in mosquitoes, birds, equines, and amphibians.
WNV was first detected in Europe in 1960. Since 1996, an induction in WNV outbreaks has been famous in Southeast and Central Europe. In recent times, an uprise in circumstances of WNV-1 and WNV-2 has been detected in Europe, which might considerably impression human and animal well being.
On this research, scientists have explored the transmission dynamics of WNV in Europe and evaluated the elements accountable for WNV transmission.
Examine design
The scientists included WNV genome sequences, ecological information, and epidemiological information into phylodynamic fashions to map the evolution and transmission historical past of WNV in Europe. They developed spatially specific phylogeographic fashions to find out the impression of various elements on viral dispersal route and velocity.
Moreover, they used a skygrid-generalized linear mannequin (GLM) to judge how modifications in environmental temperature and biodiversity could predict the variations in viral genetic range throughout the previous 20 years.
Vital observations
The research discovered distinct evolutionary pathways for WNV-1 and WNV-2 lineages and WNV-2a and WNV-2b sub-lineages in Europe. Of six lineages present in Europe, WNV-2a was recognized because the predominant sub-lineage, accounting for 73% of publicly accessible viral sequences obtained from Europe. This sublineage was discovered to unfold to no less than 14 nations.
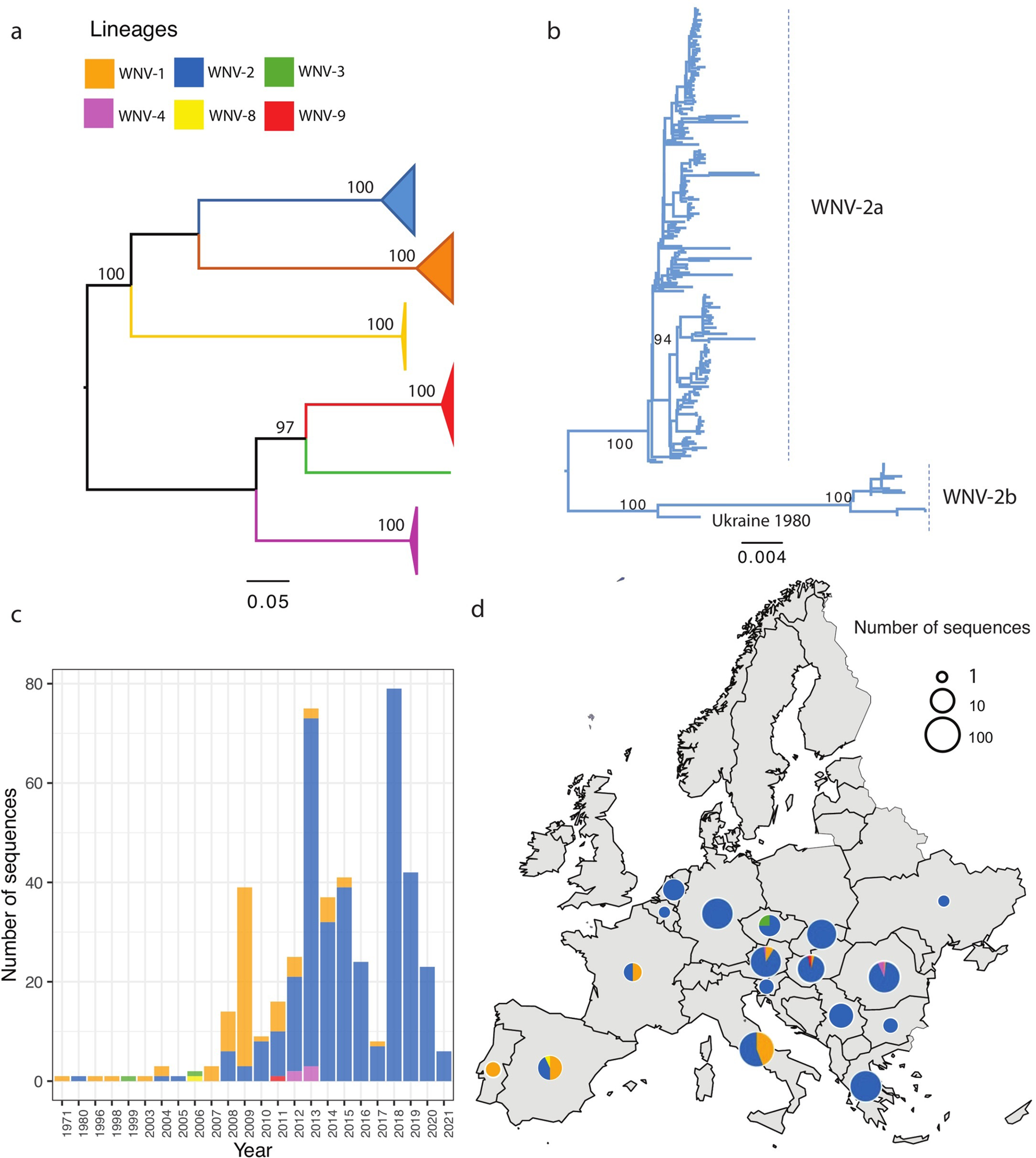 Phylogenetic evaluation of WNV full and partial nucleotide sequences detected from Europe. The evolutionary distances had been computed utilizing the optimum GTR+I mannequin, the phylogenetic tree was constructed with the Most chance (ML) methodology. Bootstrap values are given for 1000 replicates. (a) ML tree of all lineages present in Europe. The branches of lineages are all collapsed and proven as rectangles; (b) The subtree of WNV-2 sequences; (c) The WNV lineages distribution over time utilizing the identical colour exhibiting on the tree; (d) The geographical distribution of WNV lineages. Map with a small pie chart exhibiting the entire variety of sequences detected (on a logarithmic scale) per nation, with every slice proportional to the variety of distinct WNV lineages inside that nation. The European shapefile used within the research was obtained from Knowledge and Maps for ArcGIS (previously Esri Knowledge & Maps, https://www.arcgis.com/house/group.html?id=24838c2d95e14dd18c25e9bad55a7f82#overview) underneath a CC-BY 4.0 license.
Phylogenetic evaluation of WNV full and partial nucleotide sequences detected from Europe. The evolutionary distances had been computed utilizing the optimum GTR+I mannequin, the phylogenetic tree was constructed with the Most chance (ML) methodology. Bootstrap values are given for 1000 replicates. (a) ML tree of all lineages present in Europe. The branches of lineages are all collapsed and proven as rectangles; (b) The subtree of WNV-2 sequences; (c) The WNV lineages distribution over time utilizing the identical colour exhibiting on the tree; (d) The geographical distribution of WNV lineages. Map with a small pie chart exhibiting the entire variety of sequences detected (on a logarithmic scale) per nation, with every slice proportional to the variety of distinct WNV lineages inside that nation. The European shapefile used within the research was obtained from Knowledge and Maps for ArcGIS (previously Esri Knowledge & Maps, https://www.arcgis.com/house/group.html?id=24838c2d95e14dd18c25e9bad55a7f82#overview) underneath a CC-BY 4.0 license.
The research findings revealed that WNV-2a had developed into two main co-circulating clusters (clusters A and B) up to now 20 years and transmitted to the west (cluster A) and south (cluster B). Each clusters originated from Central Europe and confirmed distinct dynamic historical past and transmission patterns.
The scientists hypothesized that WNV-2a was first launched to Europe by way of long-distance migratory birds. Throughout its circulation in native fowl populations and different hosts, WNV-2a developed, diversified, and transmitted all through the European continent.
The dispersal velocity of WNV-2a was estimated to be as excessive as 88 to 215 kilometers/yr, which correlated to fowl actions. Agricultural land use was recognized as a powerful issue driving the unfold of WNV.
Particularly, the elements associated to crops and livestock manufacturing, comparable to protection of agricultural land, pasture, cultivated and managed vegetation, and livestock density, confirmed constructive associations with the dispersal velocity and transmission route of WNV. A constructive affiliation was additionally noticed between WNV transmission route, wetland protection, and migratory fowl flyways.
The scientists highlighted that the areas with high-level agricultural actions might need influenced the dispersal velocity of WNV and its route of transmission in Europe. As talked about by the scientists, high-level agricultural actions are related to a major lack of the pure ecosystem, a discount of mosquito and fowl range, and an induction of aquatic habitats. All these elements can enhance the transmission of vector-borne pathogens.
Moreover, an alteration in birds’ migration routes as a result of lack of habitats can affect the transmission of WNV to new territories. The research discovered larger transmission of WNV to city areas, the place the abundance of widespread home mosquitoes is significantly excessive due to the provision of synthetic aquatic habitats, the presence of hotter climates, and the decrease abundance of predators.
Examine significance
The research finds a excessive lineage range of WNV in Europe. Agricultural land use has the very best impression on the route and velocity of WNV transmission, which has been immediately related to urbanization and fowl habitat change.
The scientists spotlight the necessity to strengthen virological surveillance in Central Europe, the place WNV outbreaks usually tend to happen. Elevated surveillance can also be essential in areas with excessive farming density.
[ad_2]